The Future of Copper: Supply, Demand, and Alternatives
Copper is an essential metal that has become a cornerstone of modern technology and infrastructure. Its perfect electrical and thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and versatility make it invaluable across various industries. In this post, we’ll delve into the current supply and demand trends for copper, explore its applications and importance, examine historical inventory levels in Shanghai and London, and finally highlight potential substitutes as we look toward the future.
Current Copper Supply and Demand Trends
The dynamics of copper supply and demand are expected to change significantly in the coming years due to several key factors:
Rising Demand from Electrification and Renewable Energy
As the world shifts towards electrification and renewable energy, copper demand is anticipated to soar. Electric vehicles (EVs) are a prime example, requiring approximately four times more copper than conventional vehicles. Similarly, solar panels and wind turbines are heavily reliant on copper for their energy systems, fueling further demand as countries ramp up investments in sustainable practices.
Growing Urbanization
Urbanization is driving the need for modernized infrastructure in cities. Copper is essential in construction for electrical wiring and plumbing, as well as in communications infrastructure. As cities continue to expand, the demand for copper will only intensify.
Supply Constraints
Despite the increasing demand, several challenges are facing copper supply:
- Mining new copper deposits is becoming increasingly difficult, with many high-grade sources being depleted.
- Environmental regulations and social opposition can delay new project approvals, impacting supply chains.
- The geopolitical landscape presents additional risks, particularly in major producing countries like Chile and Peru.
Inventories in Shanghai and London
Monitoring inventory levels provides insight into supply and demand dynamics:
Shanghai Futures Exchange (SHFE)
- Current Inventory (November 1, 2024): 51,402 metric tons.
- Recent Trends: Inventory levels peaked at 321,695 metric tons on June 13, 2024, reflecting a significant increase from just 30,905 metric tons at the end of December 2023. This surge illustrates the seasonal nature of copper stockpiling and current market needs.
London Metal Exchange (LME)
- Current Inventory Levels: As of late 2024, LME copper inventories are at approximately 105,900 metric tons.
- Historical Context: Throughout 2024, there has been a declining trend in inventory levels, indicating a tightening supply amid rising demand. Comparatively, stock levels have decreased from higher values noted in 2023 as the market adjusts to changing consumption patterns.
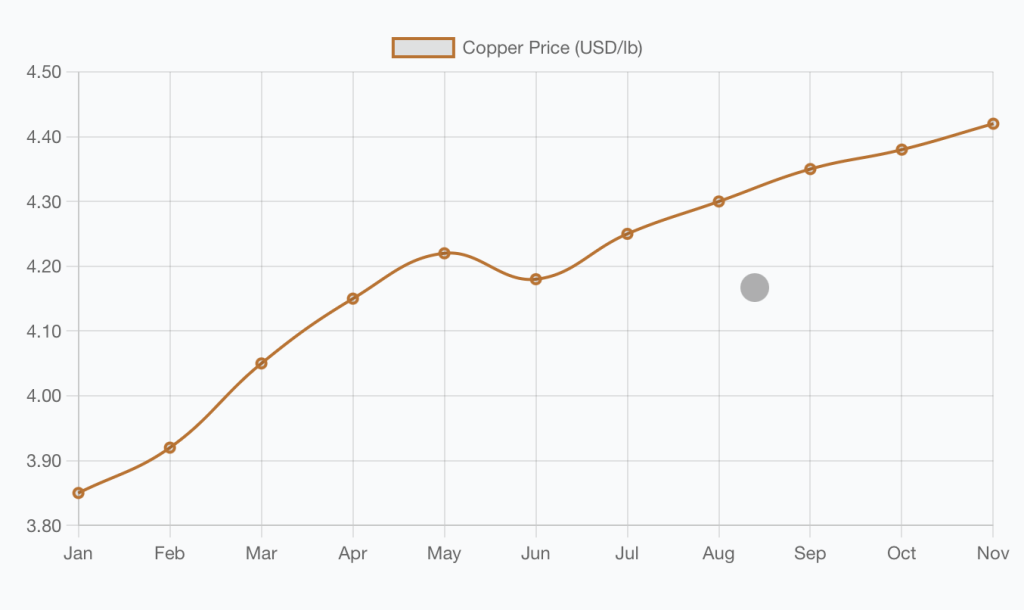
Below is an overview of the Copper price evolution until November 2024. Clearly an upward trajectory. Prices may keep going up in the next months since Copper is a key material. Lets have a look in the next section where is Copper used.
The Importance of Copper
Copper is fundamental in a range of applications:
- Electrical Wiring and Electronics: Due to its conductivity, copper is the preferred choice for wiring in homes and electrical appliances.
- Construction: Used for piping, roofing, and architectural details, copper’s durability makes it an excellent construction material.
- Renewable Energy: Copper’s role in solar panels and wind turbines highlights its importance in supporting the green energy movement.
- Healthcare: Copper’s antimicrobial properties reduce the spread of infection, making it invaluable in healthcare settings.
- Transportation: The automotive industry increasingly relies on copper as it shifts towards electric vehicles.
Main Players of the Copper Industry
The copper mining industry is dominated by several large multinational companies. Here’s a summary of the latest earnings for three of the top players:
1. Codelco
- Report Timing: Codelco’s most recent earnings were released for the first half of 2024.
- Production: The company expects to maintain copper output between 1.325 and 1.390 million tons for the year.
- Financial Performance: Codelco reported a profit dip in 2023 attributed to a decline in production, with challenges such as high operational costs impacting earnings. More details can be found here.
2. Freeport-McMoRan
- Report Timing: Freeport-McMoRan released its Q3 2024 earnings on October 22, 2024.
- Financial Results: The company reported an earnings per share (EPS) of $0.38, surpassing analysts’ expectations. Revenue showed an increase driven by higher copper prices.
- Operational Highlights: A fire incident at a new smelter in Indonesia temporarily suspended startup activities, but operational progress continues elsewhere. Further insights can be read here.
3. BHP Group
- Report Timing: BHP’s operational review for the quarter ended September 30, 2024, was announced on October 31, 2024.
- Financial Performance: BHP demonstrated strong operational performance with effective cost management. The minerals segment continued generating significant cash flows, supported by strategic investments in copper projects. You can access BHP’s latest details here.
Alternative Materials to Copper
While copper is irreplaceable in many applications, alternative materials are emerging:
- Aluminum: A lighter and more cost-effective choice for electrical applications, though less conductive.
- Silver: Extremely conductive but too expensive for widespread use. It is often used in specialized applications.
- Graphene: A promising new material with excellent properties, but still in development for mass-market applications.
- Carbon Nanotubes: Exhibiting remarkable electrical conductivity, they are still priced too high for general use.
- Fiber Optics: While not a replacement for electrical conduction, fiber optics are a superior substitute in telecommunications.
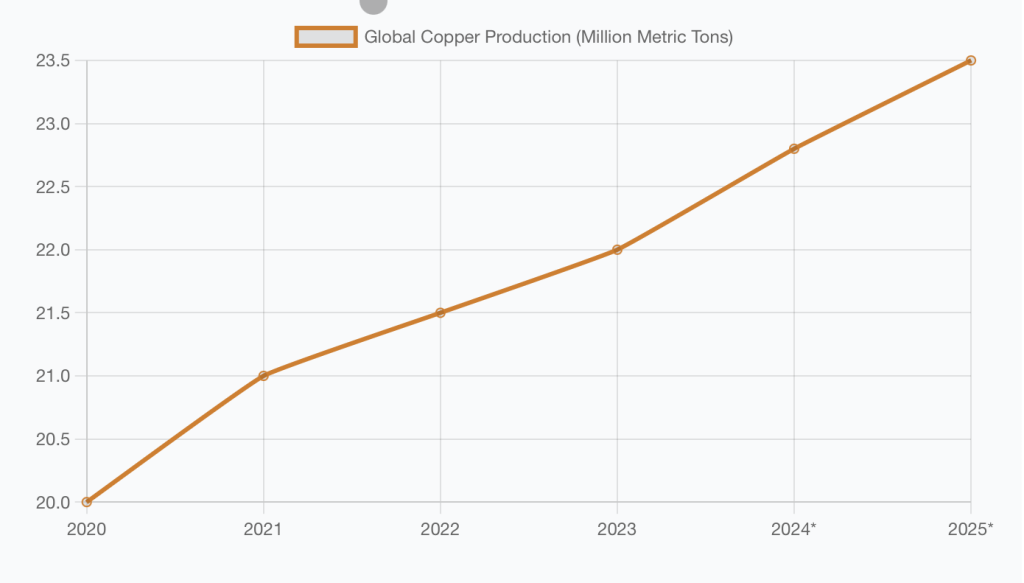
Current Global Production and Key Players
As of 2023, global copper production reached 22 million metric tons (MT), with production dominated by these key nations:
- Chile: 5 million MT (23% of global production)
- Peru: 2.6 million MT
- DR Congo: 2.5 million MT
- China: 1.7 million MT
- United States: 1.1 million MT
Notable trends include Chile’s production being at a 15-year low due to water shortages and declining investment, while the Democratic Republic of Congo continues to expand its production rapidly and may soon overtake Peru as the second-largest producer.
Global Reserves
Total identified copper reserves stand at approximately 670 million MT, distributed as follows:
- Chile: 190 million MT (28%)
- Australia: 93 million MT (14%)
- Peru: 77 million MT (11%)
- Russia: 62 million MT (9%)
- Mexico: 53 million MT (8%)
- United States: 48 million MT (7%)
Total Resources and Extraction Feasibility
The total discovered copper resources (including reserves) amount to approximately 2.8 billion MT, categorized as follows:
- Currently Economic (Proven & Probable Reserves):
- 670 million MT which is Immediately feasible for extraction. This 670 million MT meets current economic criteria
- Potentially Economic in the mid term (Measured & Indicated Resources): Approximately 1.2 billion MT. Could become viable with Technology improvements, higher copper prices and reduced operating costs
- Challenging Economics to be feasible to extract is approximately 0.9 billion MT. Currently uneconomic due to various constraints
Copper Future Outlook in the Long Term
Estimated feasible extraction timeline:
- Near-term (0-10 years): 670 million MT
- Medium-term (10-25 years): Additional 800-900 million MT
- Long-term (25+ years): Total potential of 1.5-1.8 billion MT
Production Trends:
- 2024 projected: 22.8 million MT
- 2025 projected: 23.5 million MT
- Chile expected to reach record production of 6 million MT by 2025
Looking Ahead
The copper industry faces both opportunities and challenges. While current reserves could last approximately 24 years at current production rates, technological advances, new discoveries, and improved recycling methods could significantly extend this timeline. The industry must balance increasing demand, particularly from the green energy transition, with environmental considerations and resource optimization.
The future of copper is both promising and uncertain. Copper demand will continue to rise due to its critical role in electrification and renewable energy, yet supply challenges pose significant hurdles. The trends in inventory levels in major markets such as Shanghai and London indicate tightening supply, further emphasizing the importance of monitoring these dynamics.
As we explore alternatives, such as aluminum and advanced materials like graphene and carbon nanotubes, it is essential to weigh their feasibility while recognizing that copper remains foundational in our infrastructure and technology.
Keeping an eye on these trends will help businesses, investors, and consumers navigate the evolving landscape of copper’s role in society as we move towards a sustainable future.
[Note: Data sources include USGS Mineral Commodity Summaries 2024, International Copper Study Group (ICSG), major mining companies’ reports, and industry analyses. All figures are current as of 2024.]